Extra Problems
Extra Problems
25. In the reaction below, label each reactant as a nucleophile or an electrophile. Draw the appropriate arrow(s) on the reactant side of the reaction to show the movement of electrons for how this reaction proceeds.

26. Label the electrophile and nucleophile of the following. Draw the mechanism of the reaction (two arrows) and the product it forms.

27. The triphenylmethyl cation is very stable.

a) What is the hybridization of the carbocation?
b) Specifically describe how hyperconjugation helps stabilize the triphenylmethyl cation.
c) What would happen to the stability of this cation if fluorine atoms were attached to each of the carbons of the phenyl groups? Would this cation be more or less stable? Why?
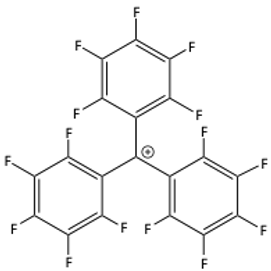
28. The following reaction occurs readily:
Experimentally, a chemist finds that if the concentration of I- is doubled, the rate doubles. Also, if the concentration of CH3Br is doubled, the rate is doubled.
a) What is the order of the reaction with respect to CH3Br?
b) What is the order of the reaction with respect to I-?
c) What is the overall rate order of the reaction?
d) Fill in the superscripts for the rate equation for this reaction: rate = k[CH3Br][ I-]
29. The following reaction was performed:
Experimentally, a chemist finds that if the concentration of (CH3)3CBr is doubled, the rate doubles. Also, the reaction rate never changed when the amount of water changes in the reaction.
a) What is the order of the reaction with respect to (CH3)3CBr?
b) What is the order of the reaction with respect to H2O?
c) What is the overall rate order of the reaction?
d) Fill in the superscripts for the rate equation for this reaction: rate = k[(CH3)3CBr][H2O]
30. Which of the following is a carbene?
a) CH2=CHCH2O-
b) Br.
c) :CCl2
d) CH3CH2+
e) NC-
31. For the following carbocations,
a) label them as methyl, primary, secondary, or tertiary.
b) If any of the carbocations are resonance stabilized, make note of that.
c) Finally, rank these carbocations in order of increasing stability.

32. For the following free radicals,
a) label them as methyl, primary, secondary, or tertiary.
b) If any of the free radicals are resonance stabilized, make note of that.
c) Then, rank these free radicals in order of increasing stability.

33. For the following carbanions,
a) label them as methyl, primary, secondary, or tertiary.
b) If any of the free radicals are resonance stabilized, make note of that.
c) Then, rank these free radicals in order of increasing stability.

34. The protons drawn on the carbon atom in between the two carbonyl groups in the following diketone are fairly acidic. Following deprotonation, the resulting carbanion is resonance stabilized. Draw the carbanion and the other good resonance forms for it.

35. When diazomethane is heated, it gives off nitrogen gas and makes a methyl carbene. Draw the Lewis structure of the methyl carbene created.

36. From the terms supplied below, insert letters in blanks that correspond to the appropriate labels. You may use a letter more than once.

____ Energy
____ Reaction coordinate
____ intermediate
____ Eact1
____ products
____ 1st transition state
____ reactants
____ rate-determining transition state
37. Sketch reaction coordinate diagrams that have the following features.
a) a 1-step reaction with an activation energy of +10 kcal/mol and a ΔH of -30 kcal/mol
b) a 1-step reaction with an activation energy of +30 kcal/mol and a ΔH of +25 kcal/mol
c) a 1-step exothermic reaction with a high activation energy
d) a 2-step reaction where the first step is the rate-determining step. The reaction is exothermic overall
38. Rank the following circled protons from least to most acidic.

39. Alcohols can be protonated to make water as a good leaving group. Once the water leaving group leaves, it forms a carbocation.

Rank the following alcohols in how quickly they will perform this reaction from the quickest (1) to the slowest (4).

