Amine and Nitrile Reactions
Amine and Nitrile Reactions
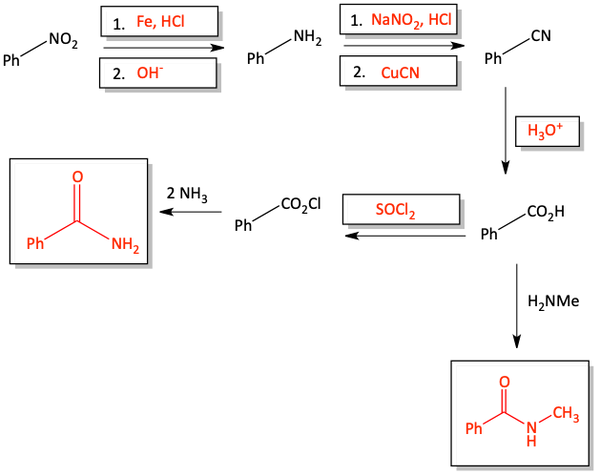
The Sandmeyer Reaction
Aniline (amino benzene) compounds are excellent precursors to make many different types of substituted benzene compounds. The amino group on an aromatic ring can be turned into the world’s greatest leaving group, N2, by reacting it with sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and HCl. Once this happens, the N2 leaving group is so good; this compound is only stable below 10°C. The N2 leaving group can be replaced with many different types of nucleophiles.

The substitution reaction is called a Sandmeyer reaction if the nucleophile is a Cu+ salt like cuprous cyanide (CuCN), cuprous chloride (CuCl), or cuprous bromide (CuBr).

Many different nucleophilic substitutions can occur. With acid and water, we get a phenol. With HBF4, we get an aromatic fluoride. With potassium iodide (KI), we get an aromatic iodide. With hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2), the N2 is replaced with a proton to make a benzene ring. You should spend some time now memorizing these reagents and products.
8. Draw the products of the following reagents with aniline (amino benzene).

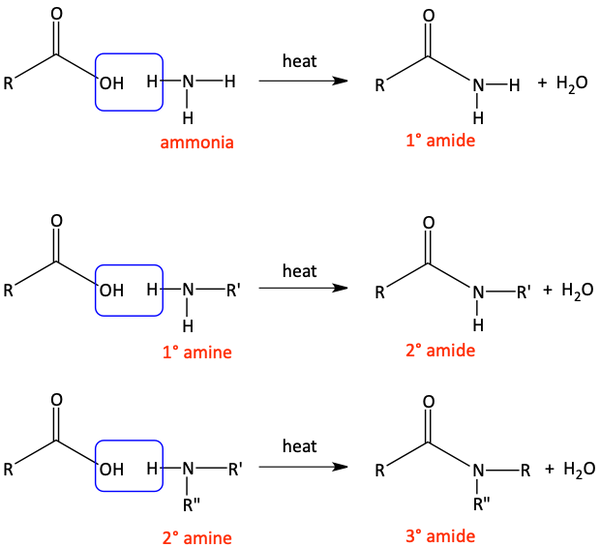
Acid chloride and amine to make amide
Perhaps the easiest way to make an amide is to react an amine with an acid chloride. The –Cl leaving group can be replaced with an amine. HCl, hydrochloric acid, is released in this reaction. That is why two equivalents of amine are used. One amine reacts with the acid chloride to make an amide and the other equivalent of amine reacts with the HCl that is produced. Acid chlorides can be easily prepared from carboxylic acids and thionyl chloride, SOCl2.

9. Draw in the appropriate products and reactants for the following reactions.
a)

b)

c)

Carboxylic acid and amine to make amide
In the previous section, we first turned a carboxylic acid into an acid chloride to perform the quick, easy reaction with an amine to form an amide. If you don’t want to take the extra time to first turn a carboxylic acid into an acid chloride, you can react the carboxylic acid directly with an amine, under heat, to form an amide. This reaction is not as easy as the reaction with an acid chloride, but it saves you one extra step in the synthesis. Water is produced in this reaction.
10. Draw in the appropriate products and reactants for the following reactions of carboxylic acids reacting with amines to make amides.
a)

b)

c)

d)

e)
Linking amino acids to make peptides
This amide synthesis from the reaction of a carboxylic acid with an amine is an important biochemical reaction.
Remember, peptides are chunks of protein. They are long chains of amino acids linked together.

These amino acids are linked together by the reaction of an amino acid carboxylic acid reacting with another amino acid amino group to make an amide. In biochemistry, the bonds that link amino acids together in peptides are called peptide bonds or peptide linkages. In organic chemistry, the functional group made in this reaction is called an amide.

11. Draw the dipeptide made from two alanine amino acids.

Ester and amine to make amide
We have seen that perhaps the easiest way to make an amide is with an acid chloride and an amine. The chloride is a great leaving group. Although it is a more difficult reaction, we can also make amides by reacting an amine with a carboxylic acid. The –OH is a worse leaving group than the chloride. Similarly, an ester can react with an amine to make an amide. The –OR alkoxy group is also not as good of a leaving group as the chloride, but the reaction does proceed with heat. Alcohol is produced in this reaction.

12. Draw in the appropriate products and reactants for the following reactions of esters reacting with amines to form amides.
a)

b)
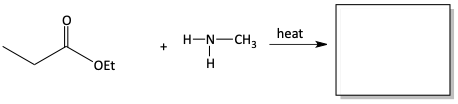
c)

d)

e)

Imine Hydrolysis
Imines have two carbon-nitrogen bonds. When imines are hydrolyzed (heated with acid and water), it forms ketones with two carbon-oxygen bonds. Notice the two carbon-nitrogen bonds form two carbon-oxygen bonds, the carbonyl, of the ketone.

Imine Hydrolysis
The negative carbon atom of a Grignard reagent can attack the partially positive carbon atom of a nitrile. The electrons go up onto the nitrogen atom, until we quench the reaction with acid water to form an imine (C=N compound). We saw in the previous section that when imines are heated up with acid and water, they undergo hydrolysis to form ketones.

13. Fill in the blank boxes with the appropriate product or reagents.
a)

b)

Hydrolysis of nitrile to carboxylic acid
Nitriles, with their three carbon-nitrogen bonds, can undergo hydrolysis to form carboxylic acids, which contain three carbon-oxygen bonds.

Hydrolysis of nitrile to carboxylic acid
On an aromatic ring, nitriles can be formed through the Sandmeyer reaction.

14. Fill in the blank boxes with the appropriate products or reagents.
a)

b)
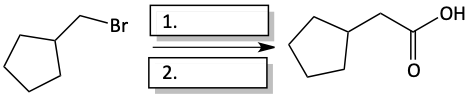
c)

d)
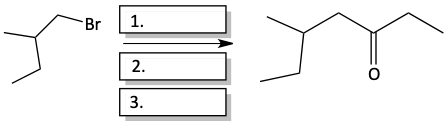
e)

Answers
8.

9.
a)

b)

c)

10.
a)

b)
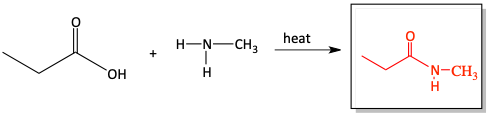
c)

d)
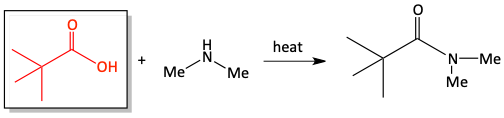
e)

11.

12.
a)

b)

c)

d)

e)

13.
a)

b)

14.
a)

b)

c)

d)
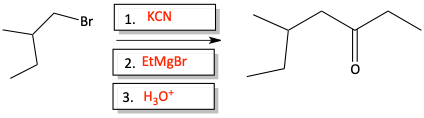
e)