Aromatic bases, pyrrole, pyridine or Heterocyclic aromatic rings
Heteroatoms like N, S, or O can extend the conjugation of the pi-system of a flat, fully conjugated ring system. It is possible to have heterocyclic aromatic ring system. Some very simple heterocyclic aromatic compounds that you should know are:

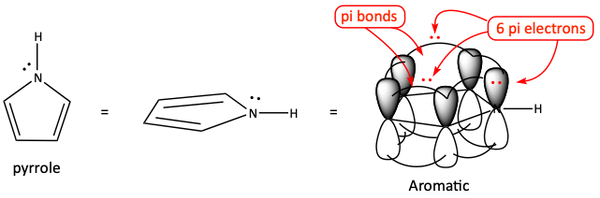
One of the lone pairs of electrons is joining in with the pi bonds to make an aromatic ring (6 pi electrons).

Basicity of nitrogen aromatics
The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atoms of most amines is usually pretty basic. Because of its partially negative charge, it can easily grab the H+ of an acid.

Even nitrogen-containing amine rings are often basic.

But, if we have a nitrogen and double bond-containing ring, the basicity can change. In these cases, we need to be a little more careful. For example, the nitrogen-containing ring, pyrrole, is not very basic. The ring has four pi-electrons from the pi bonds. It needs two more electrons to make the ring aromatic. It can get these two electrons into the pi system from the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. The nitrogen atom’s lone pair of electrons enters a p-orbital of the pi system. Notice this makes the one electron pair on the nitrogen atom delocalized over the ring. Since it is being used in the pi system to make pyrrole aromatic, the negative pair of electrons is not available to go react with the H+ of an acid, pyrrole is a very weak base. It has a pKb of 13.6.

We compare that to the nitrogen and double bond-containing ring, pyridine, which is quite basic.

The nonbonding lone pair of electrons on pyridine is not involved in the pi system. It is in an sp2 hybrid orbital pointing outside the ring. The nitrogen atom’s p-orbital that is part of the pi system is already filled with the pi electrons of the double bond attached to the nitrogen atom. The lone pair of electrons cannot go into that already filled pi system! Therefore, the nitrogen atom lone pair of electrons is localized and remains on the nitrogen atom in an sp2 hybrid orbital. That electron pair does not spread out over the ring because it is not needed to make the pyridine molecule aromatic. Those electrons are available to go and grab and H+ of an acid. Therefore, pyridine is quite basic. It has a pKb of 8.8.

In order to help determine if a nitrogen atom’s lone pair of electrons is basic or not, we look for a few things. If the nitrogen atom is not part of a ring or it is part of a ring that does not contain alkenes, it is probably pretty basic.

If the nitrogen atoms are inside of an alkene-containing double bond we need to be careful. But, if the nitrogen atom has a double bond attached to it, we can be confident that the p-orbital on that nitrogen atom would already be filled with the pi electrons of the double bond and the lone pair of electrons cannot go into the pi system. It will therefore be available to go react with an acid. That nitrogen atom would be basic. Pyrimidine has two basic nitrogen atoms because both nitrogen atoms have a double bond attached to it.

Imidazole is a nitrogen and double bond-containing ring. We need to be careful in our analysis. It has one basic nitrogen atom (with the double bond on the nitrogen). And, it has one nonbasic nitrogen atom (without a double bond on the nitrogen). The six electrons in the pi system to make this ring aromatic are the four from the two double bonds and the one from the nonbasic nitrogen atom.

7. Label each of the following nitrogen atoms as basic or nonbasic.

Answers
7.


