Bonding and Structure Problems
Extra problems
30. Identify the number of sigma and pi bonds in each of the following marked locations.

31. Homobatrachotoxin is a toxic alkaloid found in poison-dart frogs. If you put your finger in your mouth after handling such a frog, it tastes like a 9-volt battery. Identify the circled functional groups in the following molecule.
Possibilities: Alcohol, amine, nitro, nitrile, amide, ether, epoxide, ester, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid,
acid chloride, thiol, disulfide, thioether, alkane, alkene, alkyne, phenyl, phenol.

32. Write any nonzero formal charges on the following totally fictitious and crazy molecules.


33. Draw Lewis structures for the following compounds/ions:
a) CH3CO2CH3
b) acetic acid, CH3COOH
c) methanol, CH3OH
d) CH3OCH2CH3
e) acetonitrile, CH3CN
f) CH3NHCOCH3
g) (CH3)2CHCOOH
h) CH3COCH2COOCH3
i) (CH3)3COH
j) CH3CHO
k) NCCH2CH2CHO
34. Draw an acceptable line-angle structure for the compounds shown below.
a)

b)
c)
d)
35. Draw the Lewis structure (all atoms and lone pairs of electrons) for the following line-angle structures.
a)

b)

c)

d)

36. a) Draw any isomer of C5H7ClO that contains a ketone. (There are many correct answers.) b) Draw any isomer of C5H7ClO that does not contain a ketone. (Again, there are many correct answers.)
37. The structure of Vitamin C is shown here. Refer to this structure to answer the following questions.

a) Vitamin C contains _____ sp2 hybridized oxygen atom.
b) Vitamin C contains _____ sp2 hybridized carbon atoms.
c) Vitamin C contains _____ hydroxyl groups.
d) Vitamin C contains _____ sp3 hybridized carbon atoms.
e) Vitamin C contains _____ aldehyde groups.
f) Vitamin C contains _____ esters groups.
g) Vitamin C contains _____ alkene groups.
h) Vitamin C contains _____ pi bonds.
38. Refer to the following molecule to answer these questions.

a) The molecule shown below contains _______ pi bonds and ________ sigma bonds.
b) The hybridization of the oxygen atom is _____ and the O-C-C bond angle marked with an arrow is _____°.
c) This molecule contains which two of the following functional groups? (Alcohol, amine, nitrile, amide, ether, ester, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, thiol, disulfide, thioether, alkene, alkyne, phenyl, phenol)
39. Draw an example of the following:
a) an ether
b) a carboxylic acid
c) an amide
d) a nitrile
e) a phenol
f) an ester
g) a ketone
h) an aldehyde
i) an alcohol
j) an alkyne
k) an amine
l) an alkene
40. Calculate the molecular formulas for each of the following.
a)
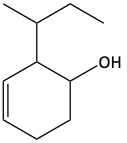
b)

c)

41. Calculate the molecular formulas for each of the following.



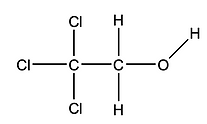


42. Identify the circled functional groups in the following molecules.
Possibilities: Alcohol, amine, nitro, nitrile, amide, ether, epoxide, ester, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid,
acid chloride, thiol, disulfide, thioether, alkane, alkene, alkyne, phenyl, phenol.


A _____________________
B _____________________
C _____________________
D _____________________
E _____________________
F _____________________
43. Which compound is more soluble in water? CH3OCH3 or CH3CH2OH? Briefly explain your choice.
44. The molecule shown below contains ___________ pi bonds and ___________ sigma bonds.

45. Which two functional groups from the following list contain a triple bond? (Alcohol, amine, nitrile, amide, ether, ester, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, acid anhydride, thiol, disulfide, thioether, alkene, alkyne, phenyl)
46. Label the formal charges on the nitrogen and oxygen atoms in the following molecule.

47. Label the hybridization of each of the nitrogen atoms in adenine (a DNA base).

48. Identify the circled functional groups in the following molecules.
Possibilities: Alcohol, amine, nitro, nitrile, amide, ether, epoxide, ester, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid,
acid chloride, thiol, disulfide, thioether, alkane, alkene, alkyne, phenyl, phenol.



A _____________________
B _____________________
C _____________________
D _____________________
E _____________________
F _____________________
G _____________________
H _____________________
49. For the following molecule (azidomethane), fill in any non-zero formal charges on the atoms.

Draw a diagram showing all of the atomic orbitals for azidomethane. Indicate which atomic orbitals overlap to form sigma bonds, which ones overlap to form pi bonds, and which ones hold lone pairs of electrons. I’ve drawn out the orbitals around N to get you started. (Note: For sake of clarity, please don’t draw the small back lobes of the hybrid orbitals).
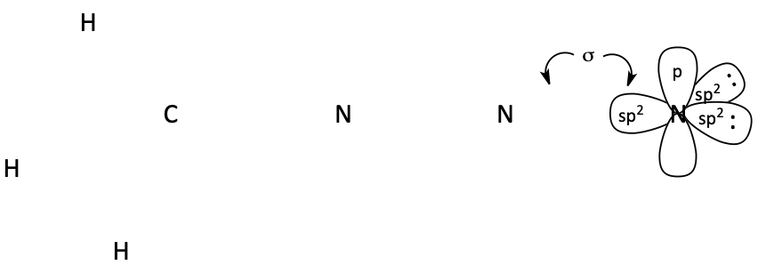
50. Draw the line-angle formula for:
CH3CH2C(CH3)2CH2CH(CH2CH3)CH2CH(CH3)2.
51. Predict the dipole moment of each of the following bonds.
a) C-O
b) C-N
c) C-Cl
d) S-O
e) C-F
52. Indicate the hybridization, the geometry, and the bond angle for the most central atom in each of the following compounds
a) CH3CH2CH3
b) CH3OCH3
c) CH3C≡N
d) CH2=CH-CH3
e) CH2=C=CH2
f) O=C=O
53. Two compounds have the formula Br-CH=CH-Br. a) Draw them both. b) Of these two isomers, one is polar and one is nonpolar. Identify the one that is polar. c) Then, explain why only one compound with the formula Br2C=CH2 exists.
54. Sketch the line-angle structures for the following oxygen-containing molecules and identify each according to its functional group. (alcohol, ether, ketone, aldehyde, carboxylic acid, phenol, or ester)
a) Cl-CH2-CHO
b) CH3CH2-O-CH3
c) (CH3)2CHCOOH
d) (CH3)3CCH2CO2CH3
e) CH3CH2COCH3
f) CH3CHOHCH2CH3
g) HO2CCH2CH3
h) (CH3)2CHCO2H
55. Draw the Lewis structure for each compound and then identify its functional group.
a)

b)
c)

d)

e)
f)
g)
h)

i)

j)
k)

l)
m)
56. For each of the following compounds identify the atoms with pi bonds between them. Identify the hybridization of these atoms. Sketch the orbitals that overlap to make sigma and pi bonds between these atoms.
a)
b)
c)

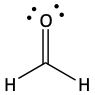
57. Which of the following pure compounds would have hydrogen bonding between the molecules? Circle them. Underline those that can hydrogen bond to water?
a) CH3-NH2
b) CH3OCH3
c) CH2=CH-CH2CH3
d) (CH3)N
e) CH3OH
f) CH3CH2CHO
g) CH3CO2H
f) CH3CO2CH3
h) CH3CONHCH2CH3
i) CH3COCH3
j) CH3CON(CH3)2
58. For each of the following pairs of compounds, identify the one with the higher boiling point.
a) CH3CH2OH and CH3OCH3
b) CH3(CH2)7CH3 and CH3(CH2)7CH2OH
c) CH3NHCH3 and CH3CH2NH2
d) HOCH2CH2CH2CH2OH and CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
e) CH3(CH2)7CH3 and CH3(CH2)3O(CH2)3CH3
f) CH3(CH2)6CH3 and (CH3CH2)4C
